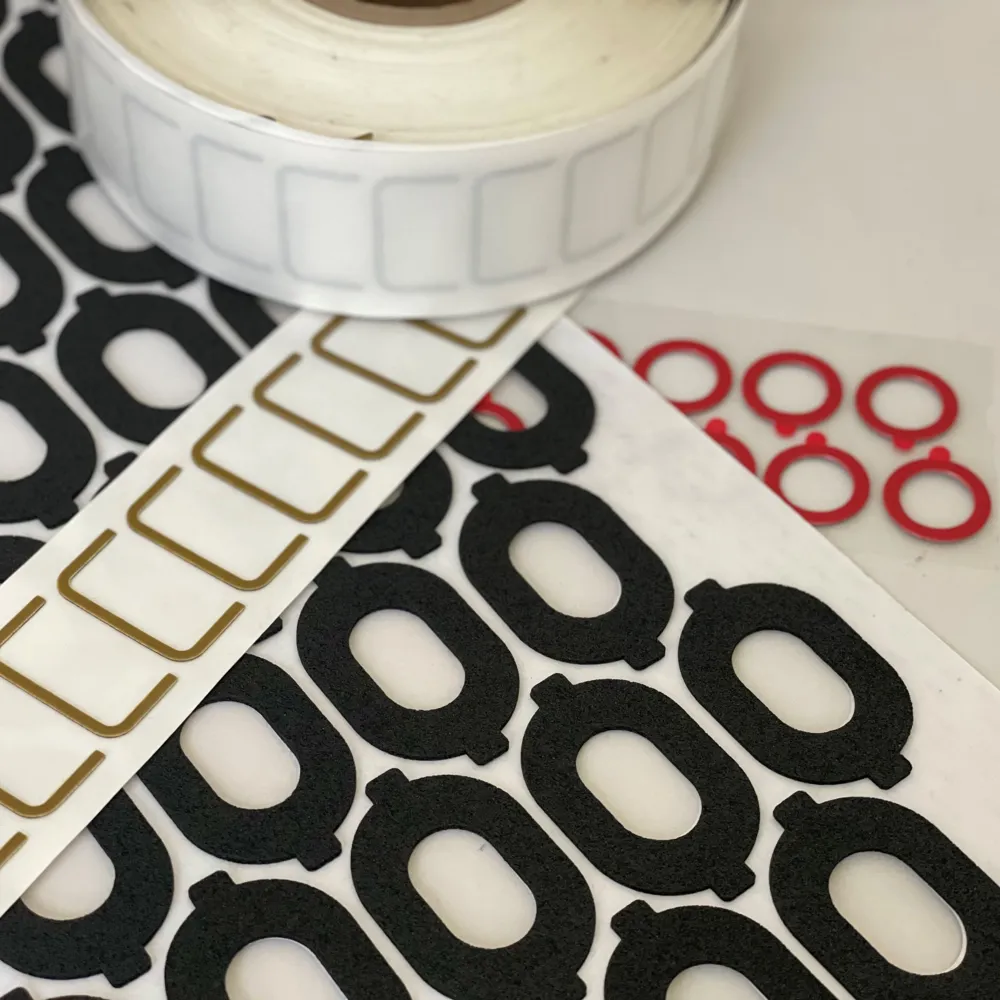

Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Foam Tapes for Custom Die-Cutting
As a flexible materials converter, we’ve seen our share of tapes and adhesives. But when it comes to flexibility and overall adaptability, it’s hard to argue against the merits of foam tapes. JBC converts both single and double-sided foam tapes for use in a wide array of markets. We’ve created custom die-cut foam tape solutions for our customers in the automotive, HVAC, appliance, electronic, medical, and industrial markets just to name a few, all designed to absorb impact, dampen vibrations, seal out the elements, and even replace mechanical fasteners. What’s that you say? You’re new to the world of foam tapes? Well then, it’s sure a good thing you’re here.
What are foam tapes?
A foam tape is exactly like it sounds, a tape comprised of a carrier (in this case a foam) backed by one or more adhesives. Carriers can have an open-cell, closed-cell, or crushed foam construction, and are made from a range of materials including polyethylene, polyurethane, neoprene sponge, PVC, cork/rubber, and specialty elastomeric composites. When it comes to adhesives, foam tapes can be either single-coated or double-coated. Single-coated tapes have adhesive on only one side of the carrier, while double-coated tapes have adhesive on both sides of the carrier.
Adhesive foam tapes are available in a variety of thicknesses, with different adhesives, carriers, and sizes all designed to meet just about every design challenge. While it varies with carrier type and adhesive chemistry, the normal temperature range that most foam tapes can withstand is -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 149°C). Foam tapes also offer excellent resistance to moisture, UV rays, and solvents, enabling them to provide high bonding strength when applied to materials of different thermal expansion coefficients.
Types of carriers used in foam tapes
The main job of the carrier in an adhesive foam tape is to provide form and support for the adhesive itself. As its name implies, it carries the adhesive load. Foam tapes can be constructed using any number of different foam carriers, and depending upon your application, they can be open-cell, closed-cell, solid rubber, or even blends. Some common examples of materials used as carriers in foam tapes are:
- EPDM/Neoprene® (ethylene propylene diene monomer)
- Polyethylene
- Polyurethane
- Microcellular urethanes
- Nitrile/NBR
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride)
- Cork
- Rubber Blends
What types of adhesives are used in foam tapes?
It wouldn’t be a foam tape without the adhesive, and when it comes to the sticky stuff, one size definitely doesn’t fit all. There are many different ways to categorize adhesives -- from the way they’re used (e.g.: permanent, repositionable, removable) to the way they perform (low surface energy, high surface energy), even their chemical makeup, but to keep things simple, let’s group them by their chemistry.
- Acrylic: Acrylic adhesives offer a nice balance of cost and performance. As a mid-range cost pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA), they are made of synthetic resins that offer a wide range of performance options. While slower to achieve full-bond strength, acrylic adhesives demonstrate high resistance to environmental factors and high temperatures.
- Rubber – Rubber adhesives provide a lower-cost PSA option and they’re often made of natural rubber compounded with tackifying resins. Rubber PSAs are typically used for indoor applications with lower surface energy substrates like polypropylene and polyethylene. Often used as assembly aids.
- Silicone – Silicone adhesives are typically the most expensive PSA option in an adhesive foam tape, so they’re usually reserved for only the most extreme applications. They are made of synthetic elastomers with inherently high-temperature resistance, UV stability flexibility. You can often find silicone adhesives being used to adhere to silicone rubber and sponge.
How are foam tapes used?
The end-uses for foam tapes are seemingly endless. Their unique construction and wide range of performance characteristics make them the ideal joining and fastening materials within industries from automotive to appliance. When it comes to cushioning, gasketing, mounting, insulating, sealing and vibration dampening, it’s hard to beat the versatility of foam tapes.
With options in foam tape density and thickness, adhesive chemistry, and cell structure, foam tapes allow for a wide variety of end uses. Even with all that flexibility, it’s critical that you pay close attention to the specific properties of each foam tape to make sure it’s well-suited for your particular application.
Foam tapes can be die-cut into custom shapes, often with complex internal geometry, that match the specific needs of a multitude of applications. Some common uses for die-cut acrylic foam tapes:
- Attaching emblems and sealing sunroofs on vehicles
- Sealing around windows in high-rise office towers
- Keeping the rain out of electrical enclosures
- Air seals in HVAC systems
- Creating air-tight spaces between panes of glass
- Minimizing BSR (buzz, squeak, and rattle) inside cars
- Replacing screws and rivets to improve aesthetics
Why die-cut foam tapes?
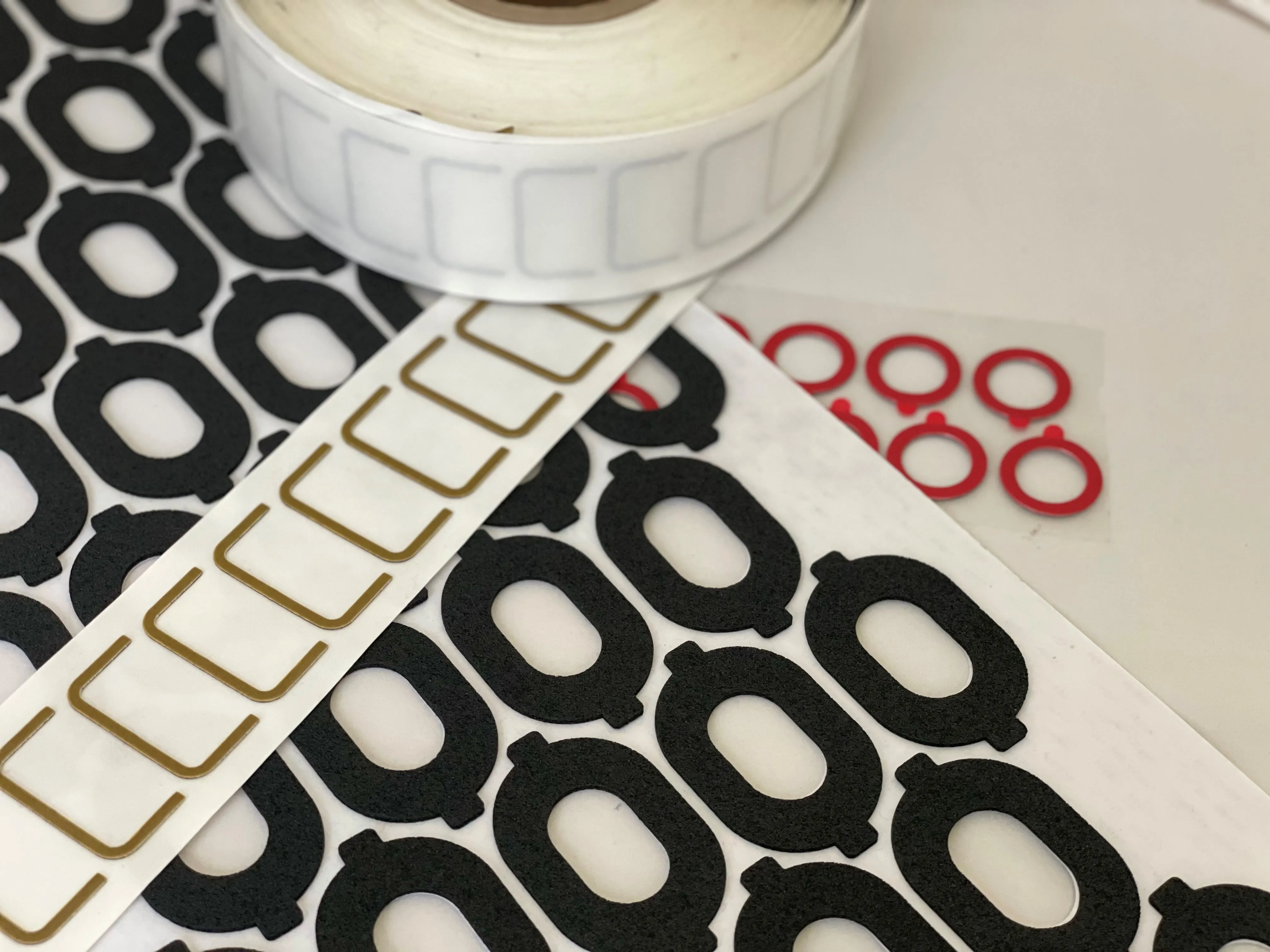

Foam tapes are typically manufactured in standard roll widths and lengths, and unless your application calls for squares and rectangles that match those standard sizes, you’re probably out of luck. That’s where JBC and custom die-cutting comes in.
Using our specially engineered flexible materials converting equipment and expertise, we can transform foam tape into any number of custom-designed shapes specifically tailored to any end-use application. Need a foam tape shaped like a 12-pointed star with four small holes in the middle? That’s die-cutting. How about some foam tape that fits inside the heated rearview mirror of your automotive OEM customer’s latest model SUV? That’s die-cutting, too. You see, die-cutting foam tapes is all about custom solutions – going from struggling to make it work to having it work every time.
Why JBC Technologies for custom die-cutting foam tapes?

JBC Technologies is your one-stop resource for precision die-cut foam tapes. Our range of flexible materials converting equipment includes high-speed, tight-tolerance rotary presses, hot and cold melt laminators, and narrow and wide web hydraulic press machines. Couple our manufacturing capabilities with our extensive team of knowledgeable and experienced process engineers and our decades-long strategic partnerships with some of the best material manufacturers in the industry, and it’s easy to see why JBC Technologies leads the way in custom die-cutting.
For additional information on how to choose the right adhesive for your die-cut foam tape, please read: A Guide to Preventing PSA Failure or Pressure Sensitive Adhesives for Die-Cut Products.
ADDITIONAL FOAM TAPE RESOURCES:
Check out the 3M™ Converter Markets Selection Guide for more product details.
Turn to JBC Technologies For Precision Cut Foam Tapes
JBC Technologies is your one-stop resource for all your foam and foam tape converting needs. For over 30 years, we've been using our industry expertise and vertically integrated converting capabilities to turn rolls of flexible materials into custom die-cut parts -- solving critical challenges for gasketing, sealing, heat shielding, thermal management, buzz, squeak and rattle/NVH, and more.